Application of Polyamine Fixing Agent FT-2 Tang Wenfeng, Fan Zenglu, Li Qing, Dou Chunxia, ​​Zhao Ruiming (School of Textiles and Materials, Xi'an Polytechnic University, Xi'an 710048, China)
Abstract: The cotton fabric dyed with direct dye and reactive dye was fixed by self-made polyamine fixing agent FT-2, and the various processing conditions in the fixing treatment were discussed and optimized. The experimental results show that the best fixing process of the fixing agent for direct dyeing of pure cotton fabric is: cotton fabric after direct dye dyeing → two dip two rolling (fixing agent 80g / L, pH of 9, the residual rate of 80 %)→pre-baking (70°C, 3min)→baking (130°C, 3min); the best fixing process for dyeing pure cotton fabrics with reactive dyes is: cotton fabric after reactive dyeing → two dip and two rolling (fixing Agent 80g / L, pH 9, rolling rate 90%) → pre-bake (70 ° C, 3 min) → baking (130 ° C, 3 min). The self-made polyamine fixing agent can improve the wet processing fastness of the dyed cotton fabric by 0.5~2, and has little effect on the color light.
Key words: polyamine fixing agent; fixing process; cotton fabric; direct dye; reactive dye CLC number: TS 193.225 Document code: A
Article ID: 1006-8341 (2011) 04-0574-07 Generally, cotton fabrics are dyed with anionic dyes such as direct dyes, reactive dyes, etc., and their wet treatment is poor in color fastness. When washed, it is not fixed on the fabric. And the hydrolyzed dye dissolves into the water, causing waste of the dye and increasing the difficulty of wastewater treatment. Therefore, the dyed fabrics generally have to undergo a fixing treatment to meet the color fastness requirements of wearing and using [1]. Since many early fixing agents contain formaldehyde or release formaldehyde, which endangers human health and pollutes the environment, people have been developing high-efficiency formaldehyde-free fixing agents [2-6]. Polyamine fixing agent is a widely used fixing agent, which has a lower cost than other new fixing agents, so it has great advantages. On the basis of the synthesis of traditional polyamine fixing agent, the synthesis method and process were innovated, and a new type of polyamine fixing agent was obtained, which improved the fixing effect of the traditional polyamine fixing agent and did not increase its cost. This paper mainly discusses the application process of self-made polyamine fixing agent, and analyzes the influence of the amount of fixing agent, pH, rolling ratio and baking temperature on the fixing effect, and the most fixing agent is obtained. Good application process parameters.
1 Experiment 1.1 Raw materials and reagents Pure cotton bleached woven fabric (industrial cotton woven fabric, specifications: C / C, 60s × 60s, 160 × 160, 58); fixing agent (homemade).
Dyes: direct fast black G (industrial products), direct red 4BS (industrial products), direct lake blue 5B (industrial products), reactive red BES (industrial products), reactive brilliant blue B-RV (industrial products). Anhydrous sodium carbonate (analytical grade), glacial acetic acid (analytical grade), sodium hydroxide (analytical grade).
1.2 Instruments and equipment SF-300 thinking computer color measuring instrument, electronic balance (sartorius, Germany), experimental small rolling car (Jiangsu Jingjiang Haishu Equipment Factory), automatic shaping dryer R-3 (Taiwan Rui Specific dyeing test machine Co., Ltd.), 800 type high speed centrifuge (Changzhou Guohua Electric Co., Ltd.), Y571B friction fastness test machine (Wenzhou Textile Instrument Factory), SW-12A wash fastness test machine (Wuxi Textile Instrument Factory) ).
1.3 Method for synthesizing fixing agent A certain amount of triethylenetetramine is added to a four-necked flask with a stirrer and placed in a cold water bath. The temperature in the flask is controlled at about 15 °C, and the stirrer is started. The pressure funnel slowly added dropwise epichlorohydrin while strengthening the cooling. After the completion of the dropwise addition, the reaction was continued for 1 hour in the cold water bath, and the dimethylamine was further added dropwise. After the completion of the dropwise addition, the reaction was continued for 1 hour, and the temperature was raised to a certain temperature for 4 hours to obtain a synthetic product. . The molar ratio of triethylenetetramine, epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine is 1:5.5:1.5.
1.4 Dyeing method (1) Direct dyeing method Process prescription: Dye dosage (o.w.f): 5%, salt: 20g/L, bath ratio: 30î—¾1, reactive dyeing process curve is shown in Figure 1. Show. 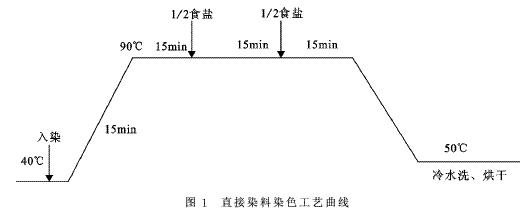
(2) Reactive dye dyeing method Process prescription: dye dosage (o.w.f) 15%, Yuanming powder 40g/L, soda ash/(g/L)10, bath ratio 30î—¾1, reactive dye dyeing process curve Figure 2 shows. 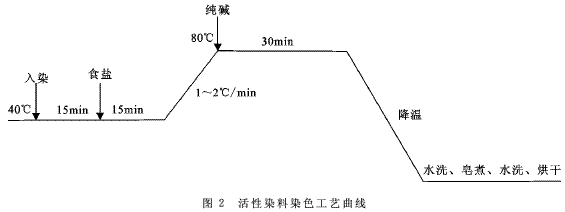
1.5 Fixing process After dyeing, cotton fabric → padding fixing finishing liquid → two dip two rolling → prebaking → baking.
1.6 Test method Determination of rubbing fastness The rubbing fastness is determined according to the method of GB/T 3920-1997 "Color fastness to rubbing of textile color fastness test".
The color fastness to soaping was measured by the color fastness tester SW-12, which was determined by the method of GB/T 3921-2008 "Color fastness to soaping test of textiles" [7-8].
Color fastness level The color fastness level is determined according to GB/T250—2008 staining with gray sample card. The chromatic aberration test was carried out by SF-300 thinking computer colorimeter to determine the ΔL, ΔC, ΔE, ΔH of the fabric, and the corresponding evaluation and analysis.
2. Results and discussion The reaction of epichlorohydrin with several polyamines was carried out to synthesize a self-made polyamine fixing agent FT-2 with a pH of about 7 and a solid content of 57.6%. Color performance was explored. In this experiment, the effects of the amount of polyamine fixing agent FT-2, pH, rolling ratio and baking temperature on the fixing effect of dyeing cotton fabric with direct dye and reactive dye were discussed.
2.1 The effect of the amount of FT-2 on the fixing effect The amount of the fixing agent has a great influence on the fixing effect. Therefore, the amount of the fixing agent is first changed to fix the color to determine the fixing agent when the effect is optimal. Dosage, and determine the most economical amount.
(1) The effect of FT-2 dosage on the fixing effect of direct dyed cotton fabrics is shown in Table 1. 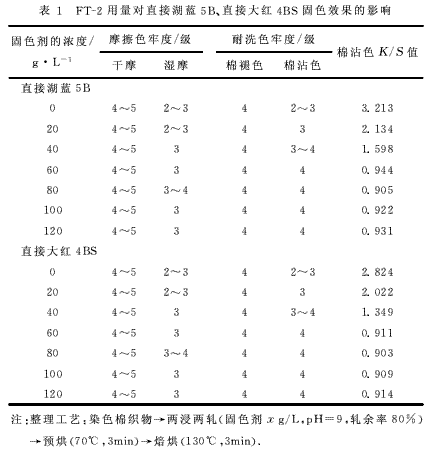
(2) The effect of FT-2 dosage on the fixing effect of reactive dyed cotton fabrics is shown in Table 2. 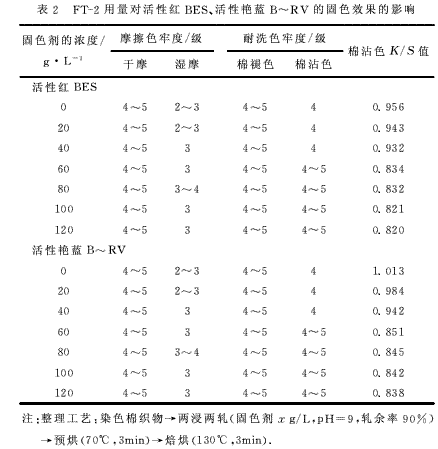
It can be seen from Table 2 that with the increase of the amount of FT-2, the color fastness of dyed fabrics is continuously improved. When the concentration is from 0g/L to 80g/L, the color fastness increases with the increase of the concentration of the fixing agent, and the dosage of the fixing agent continues to increase. After reaching 80g/L, the fastness does not change much. The amount of fixing agent for the above two direct dyes is almost the same. It may be that when the amount of fixing agent reaches 80g/L, the fixing agent can be fully reacted with fiber and dye. Reducing the amount of fixing agent will make the fixing effect worse; increasing the fixing agent dosage will not improve the fixing effect. Considering that increasing the amount of fixing agent will affect the color of the fabric, the feel and excessive use will increase the cost of production, and the dosage of fixing agent should be about 80g/L.
2.2 The effect of pH value on the fixing effect of fixing agent The pH value of the polyamine fixing agent synthesized in this subject is about 7, and the pH of the fixing fixing liquid is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 respectively. , 11, 12, 13, the results of the determination of the fixation effect are shown in Table 3, 4. 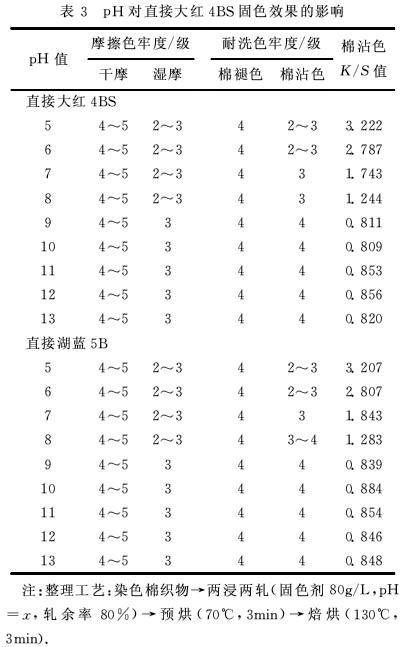

It can be seen from Tables 3 and 4 that the pH value has a great influence on the fixing effect of the fixing agent. When the pH value is less than 9, the fixing effect is obviously improved with the increase of pH value. When the PH value is greater than 9, the fixing effect is reduced. When the pH value is too low, the cotton fiber will be damaged to some extent; when the pH value is too high, the reactive dye is easily hydrolyzed, and the fastness is lowered, so the optimum fixing pH is 9.
2.3 Influence of rolling rate on fixing effect The rolling rate affects the amount of liquid on the fabric and has a great influence on the fixing effect. Therefore, the rolling rate is changed to investigate the effect of the rolling ratio on the fixing effect.
(1) Effect of rolling ratio on the fixing effect of direct dyes Direct dye dyed cotton fabrics were treated with polyamine fixing agents at different rolling ratios. The color fastness of the fabrics is shown in Table 5. 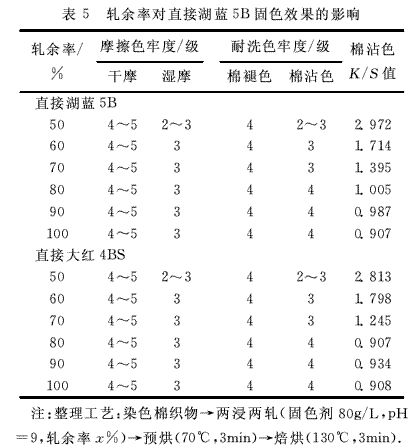
Analysis of Table 5 shows that the fixing efficiency of the fixing agent is getting better from 50% to 80%. With the increase of the rolling rate, the fixing effect is not obviously improved, and the amount of liquid in the fabric is too high, which will affect the color light and also make the drying cost higher. It can be concluded that the fixing effect of the fixing agent is best when the rolling ratio is about 80%.
(2) Effect of rolling ratio on the fixing effect of reactive dyes The reactive dye-dyed cotton fabrics were treated with polyamine fixing agents at different rolling ratios. The color fastness of the fabrics is shown in Table 6. 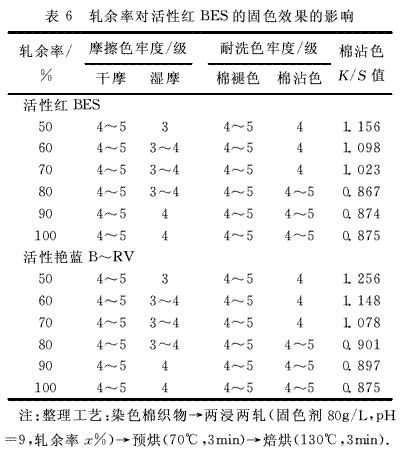
From Table 6, it is concluded that the fixing effect of the fixing agent is gradually improved from 50% to 90%, and the fixing performance is hardly improved with the increase of the rolling ratio. It is concluded that the fixing effect of the fixing agent is best when the rolling ratio is about 90%. When the rolling ratio is too low, the pressure of the equipment will be too large, which will easily cause damage to the equipment. At the same time, the rolling rate is too low, the amount of fixing agent on the fiber is too small, the fixing effect is poor, and the rolling ratio is too high. When the fixing agent on the fiber is too much, the dyeing fastness is difficult to increase, and the excessively high rolling rate will affect the drying speed of the fiber and increase the burden during drying. Within a certain range of the fabric, as the liquid-carrying rate of the fabric increases, the fixing effect of the fixing agent remaining on the fabric after rolling is better. However, after a certain amount, the liquid-carrying rate is too high, and the amount of fixing color left on the fabric is too large, which will have a great influence on the color and feel of the fabric.
2.4 Effect of baking temperature on fixing effect The fixing effect of polyamine fixing agent at different baking temperatures is shown in Table 7, 8. 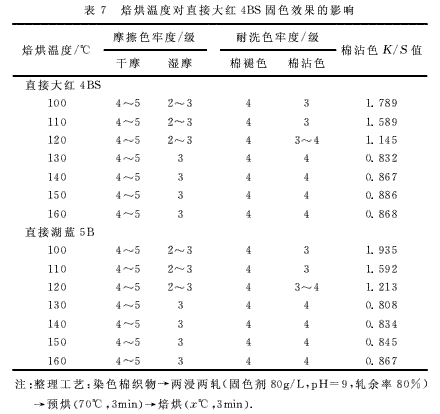
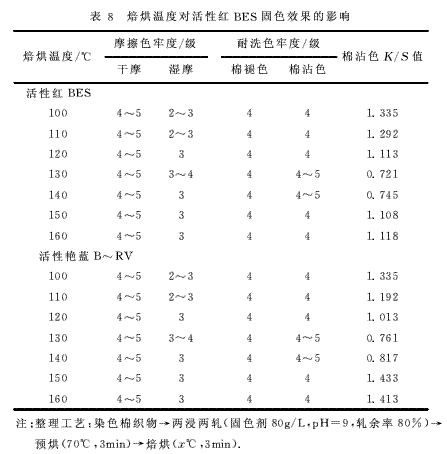
It can be seen from Tables 7 and 8 that the fixing effect is best when the baking temperature is 130 °C. When the temperature is lower or higher than 130 °C, the fixing effect is reduced. Because the temperature is too low, the fixing agent is insufficiently combined with the fiber and the dye, and it is not strong enough; when the temperature is 130 ° C, the fixing agent can fully combine with the dye to fix the dye on the fiber, and the dyeing fastness is increased. The molecular structure of the over-fixing fixative may have been destroyed, resulting in a decrease in fixing performance.
3 Conclusions (1) The best fixing process of FT-2 for direct dyes in the experiment is: dyed cotton fabric → two-dip two-rolling (fixing agent 80g/L, pH 9, rolling residual rate 80%) →Pre-bake (70 ° C, 3 min) → baking (130 ° C, 3 min). The best process for fixing the reactive dyes is: dyed cotton fabric → two-dip two-rolling (fixing agent 80g/L, pH 9, rolling ratio 90%) → pre-baking (70 ° C, 3 min) → baking ( 130 ° C, 3 min).
(2) After the dyeing of the reactive dyed cotton fabric, the dry rubbing fastness can reach 4~5 grade; the wet rubbing fastness can be improved by 0.5 grade; the soaping fastness reaches 4~5 grade.
(3) After the direct dyed cotton fabric is padded and finished by the fixing agent, the dry rubbing fastness can be improved by 0.5 to 4; the wet rubbing fastness can be improved by 0.5, reaching level 3; soaping Fastness and fading fastness increase by about 2 grades, which can reach about 4 grades.
references:
[1] Wang Chunmei, Hu Xiaolin, Li Zhaohui, et al. Development and application of reactive fixing agent [J]. Progress in Textile Technology, 2005, (6): 53-62.
[2] Li Zhanxiong, Wang Changyi. Preparation and application of a cationic aldehyde-free fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2007, 24 (12): 10-12.
[3] Li Qing, Fan Zenglu, Dou Chunxia. Synthesis and properties of reactive waterborne polyurethane fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing, 2009 (24): 1-5.
[4] Xu Lei, Zhao Zhenhe, Zhang Rong, et al. Synthesis and application of reactive dye formaldehyde-free fixing agent X02 [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2006, 23 (1): 17-18.
[5] Li Qing, Fan Zenglu, Cao Aihua. Synthesis and application of cationic waterborne polyurethane fixing agent [J]. Printing and dyeing auxiliaries, 2010, 27 (9): 29-32.
[6] He Yuxin. Dye Chemistry [M]. Beijing: China Textile Press, 2004: 58-68.
[7] Chen Ying. Dyeing and finishing process experiment tutorial [M]. Beijing: China Textile Press, 2004: 69-70.
[8] Dong Zhenli, Zheng Baohai, Qi Guifen, et al. Color measurement and electronic computer color matching [M]. 2 version. Beijing: China Textile Press, 2007: 66-70.
Metal Steel Belt Clip,Steel Spring For Slap Band,Steel Metric Measuring Tape
HENAN BONTHE MEASURING TOOLS. CO., LTD , https://www.tapemeasureb.com