The welding process optimization method is not only considered to improve the fatigue strength of the welded structure, but also has great benefits for the static load strength of the welded structure and the metallurgical properties of the welded joint. Many of the materials in this regard are not repeated here.
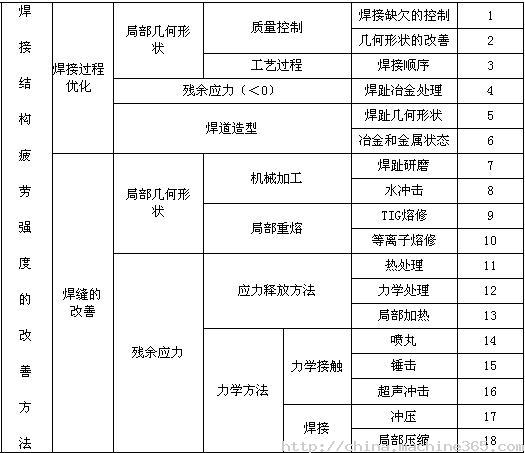
The main methods for improving the fatigue strength of welded joints are discussed in detail in three parts from the perspective of process methods.
3.1 Method for improving weld toe geometry and reducing stress concentration
3.1 .1 TIG melting repair
Research at home and abroad has shown that TIG welding can greatly improve the fatigue strength of welded joints. This method is to re-melt the transition part of the welded joint by tungsten argon arc welding method to form the weld and the base metal. Smooth transition. The stress concentration is reduced, and the minute non-metallic slag at the portion is also reduced, thereby increasing the fatigue strength of the joint portion.
The welding process requires that the welding torch is generally located 0.5 to 1.5 mm away from the weld toe, and it is necessary to keep the remelted parts clean, if it is better with a slight grinding effect. What is important is how to deal with the re-arcing when the arc is extinguished in remelting, because this will affect the quality of the reflow bead. It is generally recommended that the best position for re-arcing is 6mm before the weld crater. Recently, the International Welding Society organized some welding institutes in some European countries and Japan, and used a uniform sample prepared by the British Welding Institute to conduct a uniform study on the effectiveness of the joint fatigue strength method. The nominal fatigue strength at 2 x 106 cycles of the joint was increased by 58%, and the nominal value of the fatigue strength of 211 MPa obtained was converted into a corresponding characteristic value (K index) of 144 MPa. It is higher than the highest FAT value in the joint detail fatigue strength of the International Welding Society.
3.1 .2 Machining
If the surface of the weld is machined, the stress concentration will be greatly reduced, and the fatigue strength of the butt joint will be correspondingly improved. When the weld has no defects, the fatigue strength of the joint can be higher than the fatigue strength of the base metal. However, the cost of such surface machining is very high, so it is only suitable for the processing where it is really beneficial and can be processed. For welds with serious defects and no under-welding, the stress concentration at the defect or weld root is much more serious than the stress concentration on the weld surface, so in this case the machining of the weld surface is meaningless. of. If there is an incomplete penetration defect, the fatigue crack will not start to crack at the residual height and the weld toe, but will be transferred to the unwelded portion of the weld root. In the presence of incomplete penetration defects, machining tends to reduce joint fatigue strength.
Sometimes it is not necessary to machine the entire weld metal, but only the machining of the weld toe, which can greatly improve the fatigue strength of the joint. Studies have shown that in this case, the cracking point is not at the weld toe but is transferred to the weld defect.
The fatigue strength test of the alternating load of the transverse butt weld of high-strength steel (tensile strength σb=1080 MPa) in the former Soviet Union Makorov shows that the fatigue strength is ±150 MPa at 2×106 cycles in the as-welded condition, if the weld is When the machining process is performed to remove the residual height, the fatigue strength is increased to ±275 MPa, which is equivalent to the fatigue strength of the base metal. However, if the local grinding is performed on the weld toe, the fatigue strength is ±245 MPa, which is 83% of the machining effect. Compared with the welded state, the fatigue strength is increased by 65%, of course, whether it is machining or grinding. The method of cutting, if not carefully carried out as required, in order to ensure the processing effect, the improvement of fatigue strength is limited.
3.1 .3 grinding wheel grinding
Grinding with grinding wheels, although not as effective as machining, is also an effective way to improve the fatigue strength of welded joints. The International Welding Society recommends high-speed electric or hydraulically driven grinding wheels with a speed of (15,000~40000) r/min. The grinding wheel is made of carbon-tungsten material and its diameter should ensure that the grinding depth should be equal to or greater than 1/4 plate thickness. A recent study by the International Welding Society has shown that after grinding the sample, the nominal fatigue strength at 2 x 106 cycles is increased by 45%. If the nominal value of the obtained 199 MPa fatigue strength is converted to the corresponding characteristic value (135 MPa), Higher than the highest FAT value in the joint detail fatigue strength of the International Welding Society. It should be noted that the grinding direction should be consistent with the direction of the force line, otherwise there will be a mark perpendicular to the force line in the weld, which is equivalent to the stress concentration source, which plays a role in reducing the fatigue strength of the joint.
Previous Next
Single Wave Washer,Single-Layer Wave Springs,Nested Wave Spring,Multi-Layer Standard Wave Springs
Ningbo FLK Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.flk-global.com