The parameters of the laser beam, the performance and accuracy of the machine and the CNC system directly affect the efficiency and quality of the laser cutting. Especially for parts with high cutting precision or large thickness, the following key technologies must be mastered and solved:
1. Focus position control technology:
One of the advantages of laser cutting is that the energy density of the beam is high, generally >10 W/cm2. Since the energy density is proportional to 4/πd2, the focal spot diameter is as small as possible to produce a narrow slit; and the focal spot diameter is also proportional to the focal depth of the lens. The smaller the focal depth of the focusing lens, the smaller the focal spot diameter. However, the cutting has a splash, and the lens is too close to the workpiece to damage the lens. Therefore, the focal length of 5〃~7.5〃?(127~190mm) is widely used in industrial applications of high-power CO2 laser cutting. The actual focal spot diameter is between 0.1 and 0.4 mm. For high quality cuts, the effective depth of focus is also related to the lens diameter and the material being cut. For example, a carbon steel is cut with a 5 inch lens, and the depth of focus is in the range of +2% of the focal length, that is, about 5 mm. It is therefore important to control the position of the focus relative to the surface of the material being cut. Concerned about the cutting quality, cutting speed and other factors, in principle, the metal material <6mm, the focus is on the surface; >6mm carbon steel, the focus is above the surface; >6mm stainless steel, the focus is below the surface. The specific dimensions are determined experimentally.
There are three easy ways to determine the focus position in industrial production:
(1) Printing method: the cutting head is moved from top to bottom, and laser beam printing is performed on the plastic plate, and the smallest diameter is the focus.
(2) Inclined plate method: The plastic plate obliquely placed at an angle to the vertical axis is horizontally pulled, and the minimum point of the laser beam is focused.
(3) Blue spark method: remove the nozzle, blow the air, and pulse the laser on the stainless steel plate to move the cutting head from top to bottom until the blue spark is at the maximum focus.
For the cutting machine of the flying light path, due to the divergence angle of the beam, the length of the optical path is different when the proximal end and the distal end are cut, and the beam size before focusing has a certain difference. The larger the diameter of the incident beam, the smaller the diameter of the focal spot. In order to reduce the change of the spot size caused by the change of the beam size before focusing, the manufacturers of laser cutting systems at home and abroad provide some special devices for users to choose:
(1) Parallel light pipe. This is a commonly used method, in which a parallel light pipe is added to the output end of the CO 2 laser for beam expansion treatment, the beam diameter after the beam expansion becomes larger, and the divergence angle becomes smaller, so that the near end and the far side in the cutting working range are made. The beam size is close to the same before focusing.
(2) Adding a separate moving lens lower shaft to the cutting head, which is two independent parts from the Z axis that controls the nozzle to stand off from the material surface. When the machine table moves or the optical axis moves, the beam also moves from the proximal end to the distal F axis, so that the spot diameter remains the same throughout the processing area after the beam is focused. (pictured)
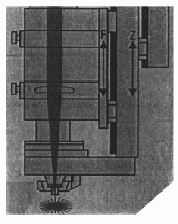
(3) Control the water pressure of the focusing mirror (generally the metal reflection focusing system). If the beam size becomes smaller before focusing and the focal spot diameter becomes larger, the water pressure is automatically controlled to change the focus curvature to make the focal spot diameter smaller.
(4) The compensation optical path system in the x and y directions is added to the flying optical path cutting machine. That is, when the optical path of the cutting distal end is increased, the compensation optical path is shortened; when the optical path of the cutting proximal end is decreased, the compensation optical path is increased to keep the optical path length consistent.
2. Cutting perforation technology:
Any kind of thermal cutting technique, except in a few cases, can start from the edge of the board, and generally a small hole must be worn in the board. Earlier on the laser stamping compound machine, a punch was used to punch out a hole, and then a laser was used to cut from the small hole. There are two basic methods for perforating a laser cutter without a stamping device:
(1) Blast drilling: (Blast drilling)
After the material is irradiated by the continuous laser, a pit is formed in the center, and then the molten material is quickly removed by the flow of oxygen coaxial with the laser beam to form a hole. Generally, the size of the hole is related to the thickness of the plate. The average diameter of the blasting perforation is half of the thickness of the plate. Therefore, the blasting hole of the thicker plate has a larger hole diameter and is not round, and it is not suitable for use on parts with high requirements (such as oil mesh joint pipe). ), can only be used on scrap. In addition, since the oxygen pressure used for the perforation is the same as that at the time of cutting, the splash is large.
(2) Pulse perforation: (Pulse drilling)
Pulsed laser with high peak power is used to melt or vaporize a small amount of material. Air or nitrogen is usually used as an auxiliary gas to reduce the expansion of pores due to exothermic oxidation, and the gas pressure is lower than that when cutting. Each pulsed laser produces only a small particle jet that is progressively deeper, so the slab perforation time takes a few seconds. Once the perforation is completed, the auxiliary gas is immediately exchanged for oxygen for cutting. Thus, the perforation diameter is small, and the perforation quality is superior to the blasting perforation The laser used for this purpose should not only have higher output power; more importantly, the time and space characteristics of the beam, so the general cross-flow CO2 laser cannot meet the requirements of laser cutting. In addition, pulse perforation requires a more reliable pneumatic control system to achieve gas type, gas pressure switching and perforation time control.
In the case of pulsed perforation, in order to obtain a high-quality incision, the transition technique from the pulse perforation of the workpiece at rest to the constant-speed continuous cutting of the workpiece should be taken seriously. In theory, it is usually possible to change the cutting conditions of the acceleration section: such as focal length, nozzle position, gas pressure, etc., but in practice it is unlikely that the above conditions are changed due to too short a time. In industrial production, the method of changing the average laser power is mainly used. The specific methods are as follows: (1) changing the pulse width; (2) changing the pulse frequency; (3) changing the pulse width and frequency at the same time. The actual results show that the (3) effect is the best.
Next page
Anti-Corrosion Pump,Anti-Corrosion Sludge Pump,High Pressure Anti-Corrosion Pump
Shenyang pump products sales co., LTD , https://www.syipsc.com