[ Huaqiang Security Network News ] With the continuous strengthening of people's security awareness, the monitoring system has developed to an unprecedented new height. The topics related to the monitoring system, such as bus cameras, telecom global eyes, electronic eyes in public places, etc., have sparked a heated discussion about personal safety and personal privacy. It can be seen that the importance of monitoring systems in today's society is self-evident. 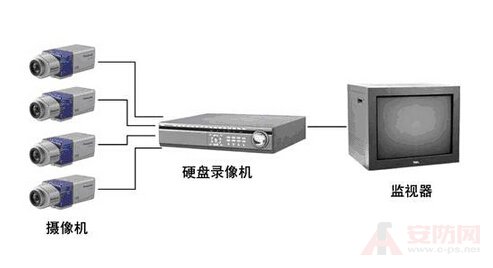 The monitoring system can be roughly divided into three parts: signal acquisition, transmission and recording. Applying different video compression formats will affect image sharpness, picture delay, and stability. The main video compression algorithms include: M-JPEG, Mpeg, H.264, Wavelet (Wavelet Compression), JPEG2000, AVS.
The monitoring system can be roughly divided into three parts: signal acquisition, transmission and recording. Applying different video compression formats will affect image sharpness, picture delay, and stability. The main video compression algorithms include: M-JPEG, Mpeg, H.264, Wavelet (Wavelet Compression), JPEG2000, AVS.
MPEG
MPEG is MovingPicturesExpertsGroup, the acronym for Dynamic Image Experts Group. The group was founded in 1988 and is responsible for establishing video and audio standards for CDs. Its members are technical experts in the fields of video, audio and systems. MPEG includes four algorithms, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and MPEG-7.
MPEG-1 was developed in 1992 and is designed for industrial standards. It can be applied to devices with different bandwidths, such as CD-ROM, Video-CD, CD-i;
MPEG-2 was established in 1994 and is designed to target image quality and higher transmission rates in advanced industry standards. In addition to being the designated standard for DVDs, it can also be used for broadcast, cable television networks, cable networks and satellite live broadcasts ( DirectBroadcastSatellite) provides broadcast-quality digital video;
MPEG3 is the encoding and compression standard originally developed by ISO/IEC for HDTV. It requires a transmission rate of 20 Mbits/sev-40 Mbits/sec, but this will cause slight distortion of the picture, and this algorithm has been eliminated due to the rapid development of MPEG2. ;
MPEG-4 has a lower transmission rate requirement and is more suitable for interactive AV services and remote monitoring than MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. This algorithm is also widely used and widely used in the field of monitoring; currently MPEG-4 compression algorithms on the market include MPEG-4ASP (Advanced SimpleProfile), MPEG-4SP (SimpleProfile), and MPEG-4 ShortHeader, which are provided by MPEG-4 ASP. I, B, Pframes, therefore, can provide a better compression ratio, while MPEG-4SP and MPEG-4 ShortHeader can only provide I, Pframes, so the bandwidth required by MPEG-4ASP is much higher than the same image quality. MPEG-4SP or ShortHeader come small. In the current practical application, MPEG-4 ASP and SP are usually used on the chip of ASIC architecture, and ShortHeader is mostly used in DSP architecture.
H.264
H.264 is also technically part of the MPEG-4 category and is the joint video group (JVT: jointvideoteam) developed by the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Active Picture Coding Experts Group (MPEG). A new digital video coding standard, which is both ITU-T H.264 and ISO/IEC Part 10 of MPEG-4. Like MPEG-4, H.264 is a widely used algorithm in the field of surveillance. Under the same image quality conditions, H.264 has higher data compression 2-3 times higher than current MPEG-2 and 1.5-2 times higher than MPEG-4. H.264 is recognized for its advancement, but it is not the preferred compression standard, especially as a monitoring product, because it also has some technical defects, such as high system resources, audio and video are not synchronized, and recorded. It takes up a lot of space.
M-JPEG
M-JPEG (Motion-Join Photographic Experts Group) technology is a motion still image (or frame-by-frame) compression technology, widely used in the field of nonlinear editing, accurate to frame editing and multi-layer image processing, using moving video sequences as continuous still images. Processing, this compression method compresses each frame completely and completely, and can store each frame randomly during the editing process, which can be edited to the frame accurately, but the M-JPEG compression efficiency is relatively low, and the space occupied by the storage is as large as each frame. 8~15K bytes, preferably only 3K bytes per frame, but if you use a high compression ratio, the video quality will be seriously reduced. In addition, the compression method of M-JPEG is not a completely unified compression standard, and there is no uniform format for codecs and storage methods of different manufacturers.
Wavelet (wavelet compression)
Wavelet transform (WAVELET) is part of the MPEG4 standard. The particularity of the algorithm in image processing mode determines its superiority in image playback and remote transmission. The resolution of the picture during playback is much higher than the compression algorithm such as MPEG4. The WAVELET algorithm uses a gradual coding method, which first encodes the entire image at a lower resolution and then gradually increases the detail. This is the same as MPEG2, which divides the image into blocks of a certain size and encodes them if different resolutions are required. , you need to split the image again and encode them one by one. The image processed by the WEVELET algorithm has a clear outline, and it is much better than other compression algorithms in recognizing the details of partial expressions and panel numbers even when the image resolution is low. WAVELET's image quality is good, and there is a linear relationship between image quality and transmission bit rate. The JPEG2000 algorithm is also developed with WAVELET as the core technology.
JPEG2000
JPEG2000, officially known as "ISO15444", is also developed by the JPEG organization. The biggest difference from the traditional JPEG is that it gives up the block coding method based on Discrete Cosine Transform, which is used by JPEG. A multi-resolution coding method based on Wavelet transform is adopted. The main purpose of wavelet transform is to extract the frequency components of the image. A higher compression ratio than JPEG can be achieved and both lossy compression and lossless compression are supported. However, there are still few applications in the monitoring system.
AVS
AVS (AudioVideocodingStandard) is China's first digital audio and video codec technology standard with independent intellectual property rights. The official name of the AVS standard in the national standard plan is "Advanced Audio and Video Coding of Information Technology". It is the first digital audio and video codec standard with independent intellectual property rights and international advanced level. Through comprehensive evaluation and comparison, AVS and H.264 have the same coding efficiency. However, due to their independent intellectual property rights, they have obvious cost advantages in related product development.

MPEG
MPEG is MovingPicturesExpertsGroup, the acronym for Dynamic Image Experts Group. The group was founded in 1988 and is responsible for establishing video and audio standards for CDs. Its members are technical experts in the fields of video, audio and systems. MPEG includes four algorithms, MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and MPEG-7.
MPEG-1 was developed in 1992 and is designed for industrial standards. It can be applied to devices with different bandwidths, such as CD-ROM, Video-CD, CD-i;
MPEG-2 was established in 1994 and is designed to target image quality and higher transmission rates in advanced industry standards. In addition to being the designated standard for DVDs, it can also be used for broadcast, cable television networks, cable networks and satellite live broadcasts ( DirectBroadcastSatellite) provides broadcast-quality digital video;
MPEG3 is the encoding and compression standard originally developed by ISO/IEC for HDTV. It requires a transmission rate of 20 Mbits/sev-40 Mbits/sec, but this will cause slight distortion of the picture, and this algorithm has been eliminated due to the rapid development of MPEG2. ;
MPEG-4 has a lower transmission rate requirement and is more suitable for interactive AV services and remote monitoring than MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. This algorithm is also widely used and widely used in the field of monitoring; currently MPEG-4 compression algorithms on the market include MPEG-4ASP (Advanced SimpleProfile), MPEG-4SP (SimpleProfile), and MPEG-4 ShortHeader, which are provided by MPEG-4 ASP. I, B, Pframes, therefore, can provide a better compression ratio, while MPEG-4SP and MPEG-4 ShortHeader can only provide I, Pframes, so the bandwidth required by MPEG-4ASP is much higher than the same image quality. MPEG-4SP or ShortHeader come small. In the current practical application, MPEG-4 ASP and SP are usually used on the chip of ASIC architecture, and ShortHeader is mostly used in DSP architecture.
H.264
H.264 is also technically part of the MPEG-4 category and is the joint video group (JVT: jointvideoteam) developed by the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Active Picture Coding Experts Group (MPEG). A new digital video coding standard, which is both ITU-T H.264 and ISO/IEC Part 10 of MPEG-4. Like MPEG-4, H.264 is a widely used algorithm in the field of surveillance. Under the same image quality conditions, H.264 has higher data compression 2-3 times higher than current MPEG-2 and 1.5-2 times higher than MPEG-4. H.264 is recognized for its advancement, but it is not the preferred compression standard, especially as a monitoring product, because it also has some technical defects, such as high system resources, audio and video are not synchronized, and recorded. It takes up a lot of space.
M-JPEG
M-JPEG (Motion-Join Photographic Experts Group) technology is a motion still image (or frame-by-frame) compression technology, widely used in the field of nonlinear editing, accurate to frame editing and multi-layer image processing, using moving video sequences as continuous still images. Processing, this compression method compresses each frame completely and completely, and can store each frame randomly during the editing process, which can be edited to the frame accurately, but the M-JPEG compression efficiency is relatively low, and the space occupied by the storage is as large as each frame. 8~15K bytes, preferably only 3K bytes per frame, but if you use a high compression ratio, the video quality will be seriously reduced. In addition, the compression method of M-JPEG is not a completely unified compression standard, and there is no uniform format for codecs and storage methods of different manufacturers.
Wavelet (wavelet compression)
Wavelet transform (WAVELET) is part of the MPEG4 standard. The particularity of the algorithm in image processing mode determines its superiority in image playback and remote transmission. The resolution of the picture during playback is much higher than the compression algorithm such as MPEG4. The WAVELET algorithm uses a gradual coding method, which first encodes the entire image at a lower resolution and then gradually increases the detail. This is the same as MPEG2, which divides the image into blocks of a certain size and encodes them if different resolutions are required. , you need to split the image again and encode them one by one. The image processed by the WEVELET algorithm has a clear outline, and it is much better than other compression algorithms in recognizing the details of partial expressions and panel numbers even when the image resolution is low. WAVELET's image quality is good, and there is a linear relationship between image quality and transmission bit rate. The JPEG2000 algorithm is also developed with WAVELET as the core technology.
JPEG2000
JPEG2000, officially known as "ISO15444", is also developed by the JPEG organization. The biggest difference from the traditional JPEG is that it gives up the block coding method based on Discrete Cosine Transform, which is used by JPEG. A multi-resolution coding method based on Wavelet transform is adopted. The main purpose of wavelet transform is to extract the frequency components of the image. A higher compression ratio than JPEG can be achieved and both lossy compression and lossless compression are supported. However, there are still few applications in the monitoring system.
AVS
AVS (AudioVideocodingStandard) is China's first digital audio and video codec technology standard with independent intellectual property rights. The official name of the AVS standard in the national standard plan is "Advanced Audio and Video Coding of Information Technology". It is the first digital audio and video codec standard with independent intellectual property rights and international advanced level. Through comprehensive evaluation and comparison, AVS and H.264 have the same coding efficiency. However, due to their independent intellectual property rights, they have obvious cost advantages in related product development.
Steel Pipe used for conveying fluid pipe, such as oil, natural gas, water, gas, steam, etc.
Steel pipe contains two types: seamless steel pipe and welded steel pipe
Steel pipe is one of our mainly produces ,made of carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel and other special metal materials as required by its customers.

Stainless Steel Pipe,Seamless Stainless Steel Pipe,316 Stainless Steel Pipe,Stainless Steel Tube
Shijiazhuang Huize Pipe Fitting Co., Ltd. , https://www.huizegd.com